- Likewise current is httpd-2.4.6-88.el7.centos.x8664 It's the other entries in the changelog after the first one (which is always the same one for CentOS, documenting what changes were made to debrand it from the RHEL version).
- Task: Show Apache httpd web server version command. Httpd is the Apache HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) server program. In order to find out apache version login to server using ssh or console. Once logged in type the following command to print the version of httpd, and then exit: # httpd -v Sample output: Server version: Apache/2.2.3 Server.
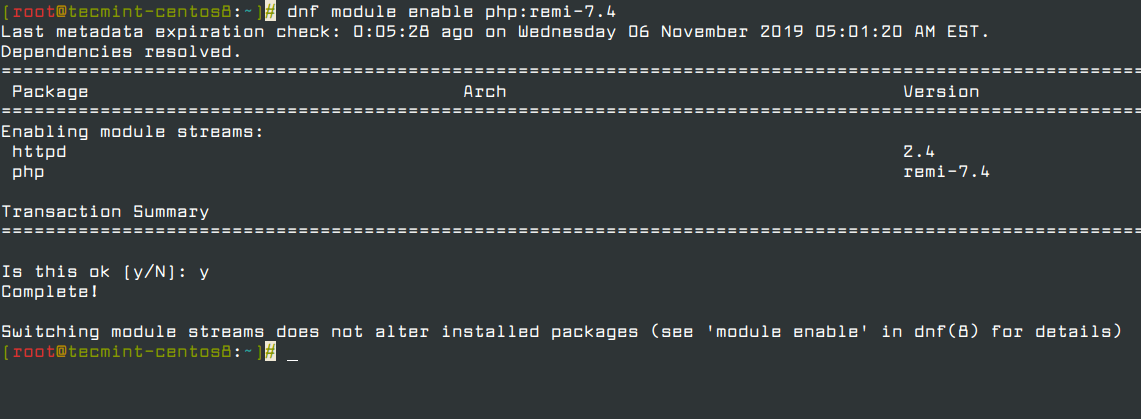
To have the latest version installed, means that your software package will probably have more new features and known bugs fixes. In this tutorial I am going to describe simple steps to install the latest Apache (httpd) version on your Centos 7 system.
Now, first of all we have find out the current version on our server. We can check it through this command:
Result:

Server version: Apache/2.4.16 (Unix)
Server built: Dec 21 2015 19:19:41
Cpanel::Easy::Apache v3.32.6 rev9999 +cloudlinux
You can get all repo at Centos.org website : http://mirror.centos.org/centos/7/
Now, before setting up the repositry you have to install EPEL.
Now to enable the centOS repositry
Once installation is done you have to start apache
The OpenBSD project has undergone a great deal of change in the past year. The open Unix-like operating system removed the Apache httpd server and replaced it with Nginx, only to sub out Nginx soon after for its own httpd server in OpenBSD 5.6, all while trying to revamp OpenSSL with its LibreSSL fork in the wake of Heartbleed.
Now OpenBSD has finally given a look at what httpd is made of and what it can do.
At AsiaBSDCon in Tokyo last week, OpenBSD developer Reyk Floeter presented attendees with an inside look at the new version of the upcoming Web server to be included with May’s OpenBSD 5.7 release. What began as an experiment by Floeter with the Relayd Web engine at last year’s g2k14 General OpenBSD Hackathon quickly evolved into httpd, a new OpenBSD server leveraging Relayd’s load-balancing application layer gateway, transparent proxy and SSL/TLS gateway—switched out with Nginx two weeks later in OpenBSD 5.6.
(Related: Which protocol will take over for HTTP?)
httpd is a secure Web server with straightforward functionality. Consisting of approximately 10,000 lines, httpd serves static files and supports FastCGI and TLS. The server has core features such as a directory listing, logging and basic authentication, but Floeter explained that OpenBSD aimed to avoid “featuritis” with a simple release and less feature requests.
The full httpd feature listing includes:
Httpd24-httpd Latest Version
- Static files: Serves static files and directories via optional auto-indexing.
- FastCGI: Supports asynchronous and direct FastCGI.
- Non-optional security: Runs are change-rooted with privilege separation by default.
- SSL/TLS: Supports secure connections via TLS powered by LibreSSL.
- Virtual servers: Uses flexible, name- and IP-based virtual servers.
- Reconfiguration: Reloads the running configuration without interruption.
- Logging: Supports per-server logging via log files or syslog.
- Blocking: Blocks, drops and redirects connections.
Httpd Latest Version
In terms of LibreSSL, OpenBSD’s “Safer TLS” fork supports more secure TLS connections in httpd with its new libtls API atop the libssl/libcrypto libraries. The server uses TLS 1.2 strong ciphers and the Perfect Forward Secrecy key-management protocol.
OpenBSD plans to add additional features, including Server Name Indication and client certificates, before httpd is officially released on May 1 along with OpenBSD 5.7.
Latest Httpd Version For Rhel 7
Floeter’s full presentation is available here.
